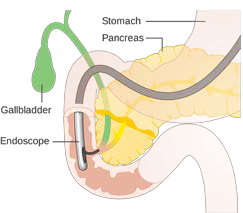
ERCP
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangio Pancreato graph (ERCP) is a technique that uses endoscopy and X-ray to view the patients’ bile and pancreatic ducts.
Reasons (Indications) for ERCP
- Bleeding per rectum.
- Blockage of bile duct by a stone.
- Blockage of bile duct by a tumor and lymphnodes.
- Blockage of bile duct by worms and other parasites.
- Damage of bile ducts during gallbladder and gastrointestinal surgery.
- Blockage of bile ducts by pancreatic cancer and by chronic pancreatitis.
- To review pain of chronic pancreatitis.
- To investigate bile and pancreatic ductal systems
ERCP preparation
- ERCP is usually an in-patient procedure.
- You should starve 8 hours before the procedure.
- Inform the doctor/Nurse of all known disease and medicine you may be taking.
- Some medication e.g. Blood thinners (anti-coagulants) may be stopped for several days before the procedure.
- Diabetic medication will need adjustment.
- You will need to be observed after the procedure, usually over 24 hours period
ERCP Procedures
The Doctor will review your medical history, medications, blood test, CTSCAN and MRI reports. ERCP procedures will be explained in details and you will be asked to sign a consent form.
Sedation – An intravenous (IV) line will be inserted into a vein in the hand/arm to administer medications. Medication once used to induce relaxation and to prevent discomfort. This is called ‘Conscious Sedation” because you are awake. For safety reasons remove your eye glasses, contact lenses and dentures.
The endoscope (duodenoscope) is placed in your mouth and advanced to the second part of the duodenum, where the opening of bile duct and pancreatic ducts are located. Using a combination of chatheters wires and X-ray on the inside of the bile duct and pancreatic duct are visualized various treatment e.g. Stone removed or placement of a stent in bile duct or pancreatic duct is then carried out.
After the procedure
Because of the sedative medicine used, the patient will take about 30 minutes – 1 hour to be fully awake. Usually most patients are observed 24 hours in the hospital. Follow-up visits will be recommended.
Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)
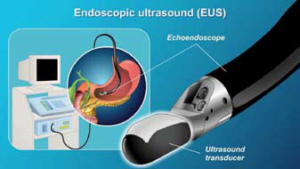 EUS is a specialized ultrasound that gives detailed information of the digestive tract. A ultrasound scanner is attached to the top of the endoscope and is able to examine the digestive tract in closer proximity.
EUS is a specialized ultrasound that gives detailed information of the digestive tract. A ultrasound scanner is attached to the top of the endoscope and is able to examine the digestive tract in closer proximity.
Reason (Indications) for EUS
- Disease of the food pipe (oesophagus).
- Disease of the stomach.
- Disease of the pancreas.
- Disease of the liver and bile ducts.
- Disease of the gall bladder.
- To take tiny specimen, fine needle aspiration (FNA) from oesophagus, stomach, pancreas and liver.
- Eus is the most accurate method to detect early cancer of the digestive tract.
Preparation for EUS
- EUS is usually an in-patient procedure.
- You should starve 8 hours before the procedure
- Inform the doctor/nurse of all known disease and medicine you may be taking.
- Some medication e.g. Blood thinners (anti-coagulants) may be stopped for several days before the procedure.
- Diabetic medication will need adjustment.
- You will need to be observed after the procedure, usually over 24 hours period
